A look at the internals of 'boxing' in the CLR
02 Aug 2017 - 1815 wordsIt’s a fundamental part of .NET and can often happen without you knowing, but how does it actually work? What is the .NET Runtime doing to make boxing possible?
Note: this post won’t be discussing how to detect boxing, how it can affect performance or how to remove it (speak to Ben Adams about that!). It will only be talking about how it works.
As an aside, if you like reading about CLR internals you may find these other posts interesting:
- How the .NET Runtime loads a Type
- Arrays and the CLR - a Very Special Relationship
- The CLR Thread Pool ‘Thread Injection’ Algorithm
- The 68 things the CLR does before executing a single line of your code
- How do .NET delegates work?
- Why is reflection slow?
- How does the ‘fixed’ keyword work?
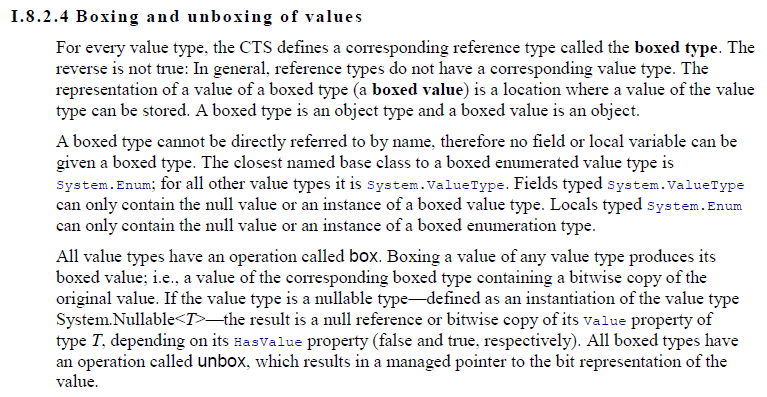
Boxing in the CLR Specification
Firstly it’s worth pointing out that boxing is mandated by the CLR specification ‘ECMA-335’, so the runtime has to provide it:
This means that there are a few key things that the CLR needs to take care of, which we will explore in the rest of this post.
Creating a ‘boxed’ Type
The first thing that the runtime needs to do is create the corresponding reference type (‘boxed type’) for any struct that it loads. You can see this in action, right at the beginning of the ‘Method Table’ creation where it first checks if it’s dealing with a ‘Value Type’, then behaves accordingly. So the ‘boxed type’ for any struct is created up front, when your .dll is imported, then it’s ready to be used by any ‘boxing’ that happens during program execution.
The comment in the linked code is pretty interesting, as it reveals some of the low-level details the runtime has to deal with:
// Check to see if the class is a valuetype; but we don't want to mark System.Enum
// as a ValueType. To accomplish this, the check takes advantage of the fact
// that System.ValueType and System.Enum are loaded one immediately after the
// other in that order, and so if the parent MethodTable is System.ValueType and
// the System.Enum MethodTable is unset, then we must be building System.Enum and
// so we don't mark it as a ValueType.
CPU-specific code-generation
But to see what happens during program execution, let’s start with a simple C# program. The code below creates a custom struct or Value Type, which is then ‘boxed’ and ‘unboxed’:
public struct MyStruct
{
public int Value;
}
var myStruct = new MyStruct();
// boxing
var boxed = (object)myStruct;
// unboxing
var unboxed = (MyStruct)boxed;
This gets turned into the following IL code, in which you can see the box and unbox.any IL instructions:
L_0000: ldloca.s myStruct
L_0002: initobj TestNamespace.MyStruct
L_0008: ldloc.0
L_0009: box TestNamespace.MyStruct
L_000e: stloc.1
L_000f: ldloc.1
L_0010: unbox.any TestNamespace.MyStruct
Runtime and JIT code
So what does the JIT do with these IL op codes? Well in the normal case it wires up and then inlines the optimised, hand-written, assembly code versions of the ‘JIT Helper Methods’ provided by the runtime. The links below take you to the relevant lines of code in the CoreCLR source:
- CPU specific, optimised versions (which are wired-up at run-time):
- JIT_BoxFastMP_InlineGetThread (AMD64 - multi-proc or Server GC, implicit TLS)
- JIT_BoxFastMP (AMD64 - multi-proc or Server GC)
- JIT_BoxFastUP (AMD64 - single-proc and Workstation GC)
- JIT_TrialAlloc::GenBox(..) (x86), which is independently wired-up
- JIT inlines the helper function call in the common case, see Compiler::impImportAndPushBox(..)
- Generic, less-optimised version, used as a fall-back MethodTable::Box(..)
- Eventually calls into CopyValueClassUnchecked(..)
- Which ties in with the answer to this Stack Overflow question Why is struct better with being less than 16 bytes?
Interesting enough, the only other ‘JIT Helper Methods’ that get this special treatment are object, string or array allocations, which goes to show just how performance sensitive boxing is.
In comparison, there is only one helper method for ‘unboxing’, called JIT_Unbox(..), which falls back to JIT_Unbox_Helper(..) in the uncommon case and is wired up here (CORINFO_HELP_UNBOX to JIT_Unbox). The JIT will also inline the helper call in the common case, to save the cost of a method call, see Compiler::impImportBlockCode(..).
Note that the ‘unbox helper’ only fetches a reference/pointer to the ‘boxed’ data, it has to then be put onto the stack. As we saw above, when the C# compiler does unboxing it uses the ‘Unbox_Any’ op-code not just the ‘Unbox’ one, see Unboxing does not create a copy of the value for more information.
Unboxing Stub Creation
As well as ‘boxing’ and ‘unboxing’ a struct, the runtime also needs to help out during the time that a type remains ‘boxed’. To see why, let’s extend MyStruct and override the ToString() method, so that it displays the current Value:
public struct MyStruct
{
public int Value;
public override string ToString()
{
return "Value = " + Value.ToString();
}
}
Now, if we look at the ‘Method Table’ the runtime creates for the boxed version of MyStruct (remember, value types have no ‘Method Table’), we can see something strange going on. Note that there are 2 entries for MyStruct::ToString, one of which I’ve labelled as an ‘Unboxing Stub’
Method table summary for 'MyStruct':
Number of static fields: 0
Number of instance fields: 1
Number of static obj ref fields: 0
Number of static boxed fields: 0
Number of declared fields: 1
Number of declared methods: 1
Number of declared non-abstract methods: 1
Vtable (with interface dupes) for 'MyStruct':
Total duplicate slots = 0
SD: MT::MethodIterator created for MyStruct (TestNamespace.MyStruct).
slot 0: MyStruct::ToString 0x000007FE41170C10 (slot = 0) (Unboxing Stub)
slot 1: System.ValueType::Equals 0x000007FEC1194078 (slot = 1)
slot 2: System.ValueType::GetHashCode 0x000007FEC1194080 (slot = 2)
slot 3: System.Object::Finalize 0x000007FEC14A30E0 (slot = 3)
slot 5: MyStruct::ToString 0x000007FE41170C18 (slot = 4)
<-- vtable ends here
So what is this ‘unboxing stub’ and why is it needed?
It’s there because if you call ToString() on a boxed version of MyStruct, it calls the overridden method declared within MyStruct itself (which is what you’d want it to do), not the Object::ToString() version. But, MyStruct::ToString() expects to be able to access any fields within the struct, such as Value in this case. To make that possible, the runtime/JIT has to adjust the this pointer before MyStruct::ToString() is called, as shown in the diagram below:
1. MyStruct: [0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00]
| Object Header | MethodTable | MyStruct |
2. MyStruct (Boxed): [0x40 0x5b 0x6f 0x6f 0xfe 0x7 0x0 0x0 0x5 0x0 0x0 0x0]
^
object 'this' pointer |
| Object Header | MethodTable | MyStruct |
3. MyStruct (Boxed): [0x40 0x5b 0x6f 0x6f 0xfe 0x7 0x0 0x0 0x5 0x0 0x0 0x0]
^
adjusted 'this' pointer |
Key to the diagram
- Original
struct, on the stack - The
structbeing boxed into anobjectthat lives on the heap - Adjustment made to this pointer so
MyStruct::ToString()will work
(If you want more information on .NET object internals, see this useful article)
We can see this in action in the the code linked below, note that the stub only consists of a few assembly instructions (it’s not as heavy-weight as a method call) and there are CPU-specific versions:
- MethodDesc::DoPrestub(..) (calls
MakeUnboxingStubWorker(..)) - MakeUnboxingStubWorker(..) (calls
EmitUnboxMethodStub(..)to create the stub)
The runtime/JIT has to do these tricks to help maintain the illusion that a struct can behave like a class, even though under-the-hood they are very different. See Eric Lipperts answer to How do ValueTypes derive from Object (ReferenceType) and still be ValueTypes? for a bit more on this.
Hopefully this post has given you some idea of what happens under-the-hood when ‘boxing’ takes place.
Further Reading
As before, if you’ve got this far you might find these other links interesting:
Useful code comments related to boxing/unboxing stubs
- MethodTableBuilder::AllocAndInitMethodDescChunk(..)
- MethodDesc::FindOrCreateAssociatedMethodDesc(..) (in genmeth.cpp)
- Compiler::impImportBlockCode(..)
- Note on different ‘Boxing’ modes, added as part of the work on JIT: modify box/unbox/isinst/castclass expansions for fast jitting
GitHub Issues
- Question: Boxing on stack for function calls
- Boxing Cache?
- Improve the default hash code for structs (read the whole discussion)
- JIT: Fix value type box optimization
- (Discussion) Lightweight Boxing?
Other similar/related articles
- .NET Type Internals - From a Microsoft CLR Perspective (section on ‘Boxing and Unboxing’)
- C# value type boxing under the hood (section on ‘Interface call into the value type instance method’)
- Value type methods – call, callvirt, constrained and hidden boxing
- Performance Quiz #12 – The Cost of a Good Hash – Solution (Rico Mariani)
- To box or not to box (Eric Lippert)
- Beware of implicit boxing of value types
- Method calls on value types and boxing
Stack Overflow Questions
- CLR specification on boxing
- How CLR works when invoking a method of a struct
- boxing on structs when calling ToString()
- Does calling a method on a value type result in boxing in .NET?
- Why does implicitly calling toString on a value type cause a box instruction
- Why is struct better with being less than 16 bytes
- When are Type Objects for Value Types created?
- If my struct implements IDisposable will it be boxed when used in a using statement?
- When does a using-statement box its argument, when it’s a struct?